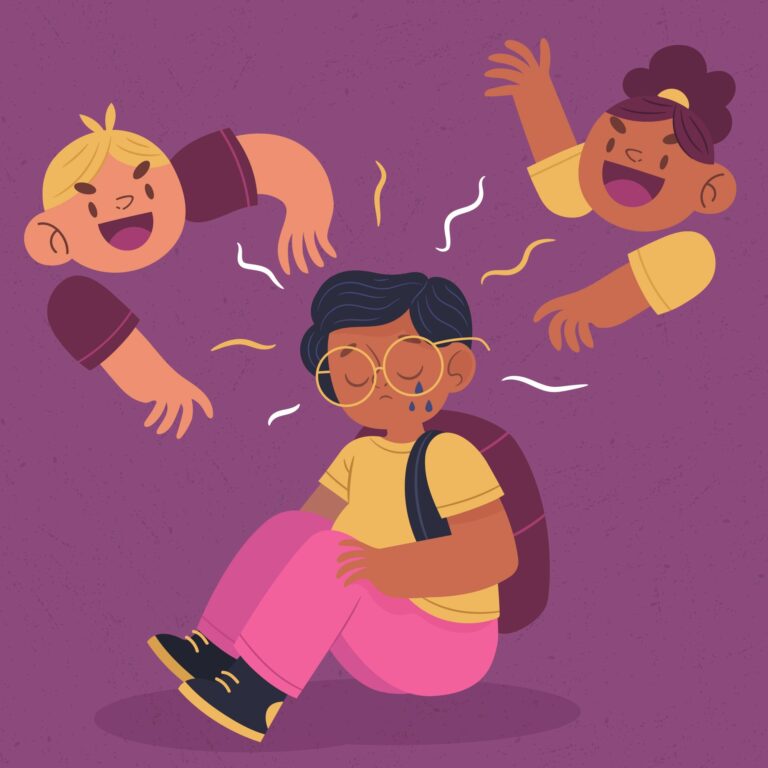
Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) is often associated with hyperactivity, inattention, and impulsivity. However, another critical yet under-discussed symptom is emotional dysregulation—the difficulty managing emotional responses in proportion to the situation. For children with ADHD, emotional dysregulation can lead to heightened emotional responses, frustration, and challenges in maintaining relationships and academic success.
Understanding how ADHD impacts emotional regulation can empower parents, educators, and caregivers to better support affected children, fostering improved emotional resilience and well-being.
Understanding Emotional Dysregulation in ADHD
What is Emotional Dysregulation?
Emotional dysregulation refers to a child’s inability to control or modulate emotional responses, often resulting in disproportionate reactions. These can include:
- Intense outbursts of anger.
- Frustration over minor inconveniences.
- Difficulty calming down after being upset.
Why is Emotional Dysregulation Common in ADHD?
ADHD affects brain regions like the prefrontal cortex, which governs executive functions such as emotional regulation, planning, and decision-making. This neurological difference makes it harder for children with ADHD to recognize, understand, and regulate their emotions effectively.
Causes of Emotional Dysregulation in Children with ADHD
1. Neurological Differences
The ADHD brain often struggles with processing and managing emotional stimuli. Reduced activity in brain areas responsible for self-regulation leads to heightened emotional responses.
2. Executive Function Deficits
Executive functions, such as working memory and inhibitory control, are critical for regulating emotions. Deficits in these areas mean children with ADHD may react impulsively before assessing their emotions.
3. Sensory Overload
Children with ADHD are often more sensitive to environmental stimuli, leading to overwhelming emotional responses to sights, sounds, or textures.
4. Frustration from ADHD Symptoms
Repeated struggles to meet academic, social, or behavioral expectations can lead to feelings of inadequacy, further intensifying emotional dysregulation.
Signs of Emotional Dysregulation in Children with ADHD
- Frequent Emotional Outbursts: Intense anger or sadness over small triggers.
- Difficulty Calming Down: Struggles to self-soothe after an emotional episode.
- Mood Swings: Rapid transitions between emotional states.
- Social Challenges: Difficulty maintaining friendships due to overwhelming reactions.
- Inability to Express Emotions Effectively: Frustration from not articulating feelings clearly.
Solutions for Managing Emotional Dysregulation
1. Behavioral Therapy
Behavioral therapy, including Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT), helps children identify and manage their emotions by teaching strategies to reframe negative thoughts and respond calmly to triggers.
2. Parent Training Programs
Parent-focused programs equip families with skills to handle emotional outbursts, establish clear boundaries, and reinforce positive behavior.
3. Mindfulness Practices
Mindfulness techniques, such as deep breathing or grounding exercises, help children develop awareness of their emotions and learn to manage stress effectively.
4. Routine and Structure
Establishing predictable daily routines reduces uncertainty and creates a sense of stability for children with ADHD.
5. Emotional Coaching
Teaching children to recognize, label, and understand their emotions builds self-awareness and enhances their ability to regulate feelings in challenging situations.
6. Professional Support
Consulting mental health professionals who specialize in ADHD can provide tailored strategies to address emotional dysregulation.
How Pathformers Supports Emotional Regulation
At Pathformers, we offer expert-designed courses tailored to address emotional dysregulation in children with ADHD:
- Mastering Emotional Regulation: Equips children with practical tools to identify and manage emotions.
- Mindfulness and ADHD: Integrates mindfulness techniques into daily life to promote emotional balance.
- Parent Support for Emotional Growth: Workshops designed to help parents create nurturing environments that foster emotional resilience.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: How does ADHD cause emotional dysregulation in children?
ADHD impacts brain areas responsible for self-regulation, making it harder for children to process and manage emotions effectively.
Q2: What are some early signs of emotional dysregulation in children with ADHD?
Signs include frequent mood swings, difficulty calming down, and intense emotional reactions disproportionate to the situation.
Q3: Can emotional dysregulation in children with ADHD improve over time?
Yes, with proper interventions such as therapy, structured routines, and emotional coaching, children can develop better emotional regulation skills.
Q4: How can parents help their child with ADHD manage emotional dysregulation?
Parents can support their child by maintaining consistent routines, modeling calm behavior, using positive reinforcement, and encouraging open discussions about emotions.
Q5: Is medication effective in managing emotional dysregulation in children with ADHD?
While medication may help address core ADHD symptoms, it is most effective when combined with behavioral strategies and therapy.
Take the Next Step in Supporting Your Child
Equip your child with the tools they need to thrive emotionally and socially. Explore Pathformers’ expert-designed courses to empower your child with strategies for managing emotional dysregulation effectively. Together, we can help them build a brighter, more balanced future.