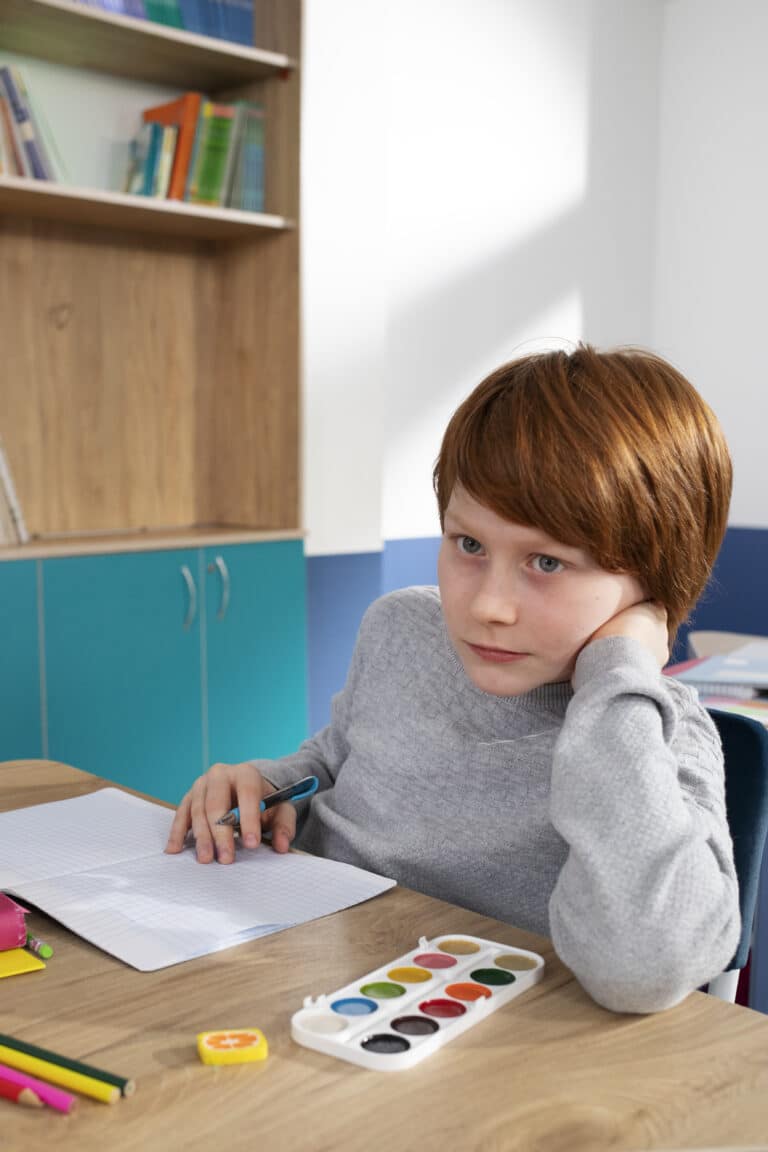
Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) can manifest through symptoms of ADHD such as inattention and behavior therapy together can provide a comprehensive approach to treat ADHD. hyperactivity. is a prevalent neurodevelopmental condition in children, characterized by inattention, hyperactivity, and impulsivity. Behavioral treatments are essential in managing ADHD symptoms, offering children strategies to navigate daily challenges effectively.
Understanding Behavioral Therapy for ADHD
Behavioral therapy focuses on modifying specific behaviors by reinforcing desired actions and reducing unwanted ones. In the context of ADHD, it equips children with skills to manage their symptoms, improve functioning, and enhance relationships.
Top Behavioral Treatments for Children with ADHD
1. Parent Training in Behavior Management
Parents learn techniques to encourage positive behavior and manage undesirable actions. This training is particularly effective for young children with ADHD, as parents play a pivotal role in their development.
- The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommends parent training as the first line of treatment for children under six.
2. Behavioral Classroom Interventions
Teachers implement strategies to support children with ADHD in the educational setting. This includes:
- Structured routines
- Clear expectations
- Positive reinforcement
These methods enhance academic performance and behavior. The American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) suggests incorporating behavioral classroom interventions as part of a comprehensive treatment plan.
3. Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
CBT helps children recognize and modify negative thought patterns, improving self-control and problem-solving skills.
- While traditionally used for mood disorders, CBT can benefit children with ADHD, especially those with co-occurring conditions like anxiety.
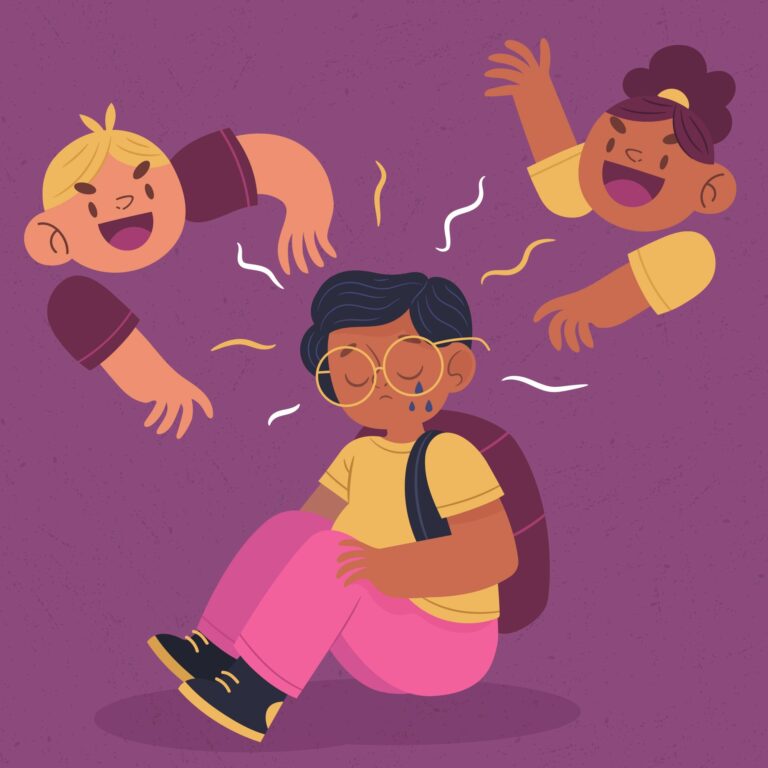
4. Social Skills Training
This therapy assists children in developing appropriate social behaviors, enhancing peer relationships, and reducing social challenges associated with ADHD.
- Through role-playing and modeling, children learn to interpret social cues and respond appropriately.
5. Behavioral Peer Interventions
Engaging in behavior therapy can significantly help your child. group therapy with peers allows children to:
- Practice new skills in a supportive environment.
- Foster social development and reduce feelings of isolation.
Such interventions can improve social interactions and build friendships.
Integrating Behavioral Treatments with Other Interventions
Combining behavioral therapies with medication often yields the best outcomes for children with ADHD.
- Stimulant and non-stimulant medications can alleviate core symptoms, while behavioral therapies address functional impairments.
- The CDC recommends a combined approach for children aged six and older.
The Role of Parents and Caregivers
Active involvement of parents and caregivers is crucial in the success of behavioral treatments.
- By participating in training programs, maintaining consistent routines, and providing positive reinforcement, they create a supportive environment conducive to their child’s progress.
Addressing Anxiety in Children with ADHD
Children with ADHD may experience anxiety, exacerbating their challenges.
- Behavioral therapies, particularly CBT, are effective in managing anxiety by teaching coping mechanisms and reducing avoidance behaviors.
- Early intervention is vital to prevent the escalation of anxiety symptoms.
Pathformers’ Courses for Parents and Children
At Pathformers, we offer specialized courses designed to support children with ADHD and their families:
- Parent Training Workshops: Equip parents with strategies to manage their child’s behavior effectively.
- Child-Focused CBT Programs: Help children develop coping skills to manage ADHD and associated anxiety.
- Social Skills Groups: Provide a platform for children to practice and enhance their social interactions.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. What is the most effective behavioral treatment for a child with ADHD?
Parent training in behavior management is highly effective, especially for young children. It empowers parents to implement strategies that promote positive behavior. (CDC)
2. Can behavioral therapy replace medication for ADHD?
For children under six, behavioral therapy is recommended as the first line of treatment. For older children, a combination of behavioral therapy and medication often provides the best results. (CDC)
3. How can I support my child during behavioral therapy?
Active participation in training sessions, consistency in applying strategies at home, and open communication with therapists will support your child’s progress.
4. Are there side effects associated with behavioral therapies?
Behavioral therapies are essential components of effective ADHD treatment. generally safe and focus on skill development. Unlike medications, they do not have physical side effects.
5. How long does it take to see improvements with behavioral therapy?
The timeline varies; some children may show improvement within a few weeks, while others may take ADHD medication to manage their symptoms. several months. Consistency and active participation are key factors.
Empower Your Child’s Future
Equip your child with the tools they need to succeed. Enroll in Pathformers’ specialized programs today to take the first step toward effective ADHD management.
Contact Us Today
Let Pathformers guide your family with proven strategies and expert support for ADHD management. Together, we can create a brighter future.